Abstract
Background: CD19 targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies showed remarkable responses in treating relapsed/refractory lymphomas. However, exorbitant cost and toxicities associated with available products limits the access in Lower-middle income countries (LMICs). Recently, we developed a novel humanized anti-CD19 CART-cell therapy and showed favorable balance of efficacy to toxicity in pre-clinical model (Dwivedi et al Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 May;20 (5):846-858.) (PCT/IN 2019/050111). Here, we report the results from our phase I study.
Materials and Methods A humanized second generation anti-CD19 CAR construct (HCAR19) with 4- 1BB co-stimulatory domain was developed at IIT Bombay. The phase I clinical trial was conducted at Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai between May 05,2021 and May 13, 2022 after obtaining regulatory approvals.
Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, whose best response to their last therapy was stable/progressive disease (SCHOLAR-1 criteria), with performance status of 0 to 1, age ≥ 18 years and adequate organ function were eligible. Those with CNS involvement were excluded.
A total of 14 participants were enrolled in this study after obtaining informed consent. These patients were enrolled sequentially as per the regulatory requirement. A 10-ml blood sample was sent to the manufacturing site to assess feasibility of CAR T generation (defined as a 4-fold expansion or 2% transduction efficiency). Later leukapheresis was done and mean duration for HCAR 19 manufacturing was 7 days. Bridging chemotherapy was allowed if indicated. Patients were admitted 7 days prior to the infusion. Lymphodepleting conditioning regimen of Fludarabine at 30mg/m2/day x 3 days and cyclophosphamide at 500 mg/m2/day x 2 days(n=5) or x 3 days after an amendment (n=5) was given to the patients starting 5 days prior to infusion.
HCAR19 dose ranging from 1x107 to 5x109 CAR-T cells was delivered in a split dose, 10% on day 0, 30% on day 1, and 60% on day 2. Patients remained hospitalized till day 7 or until all CAR-T therapy-related non-hematologic toxicities returned to baseline or grade ≤1. The primary endpoint was patient safety defined by dose limiting toxicities till 28 days post HCAR19 infusion. The secondary endpoints were response rates, duration of response, and persistence of CAR T cells, overall survival, progression free survival and dose manufacturing feasibility. CRS and ICANS were graded as per the ASTCT grading system.
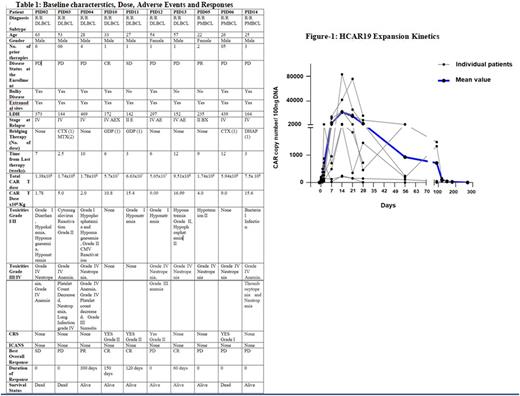
Results: Of the 14 patients enrolled in the study, 10 patients received HCAR19 infusion and were evaluable for safety and efficacy. Remaining 4 patients were withdrawn, 3 due to poor GC and 1 failed manufacturing feasibility. The average time from enrollment to infusion was 42 days (Range 13-130 days). HCAR19 cells were manufactured with transduction efficiency of 31.9 ± 4.86% (Mean ± SEM). The baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Out of 10 participants infused with HCAR19, the dose ranged from 5.7 x 107 to 7.5 x 108 CART cells. 7 patients received doses > 5x106 HCAR19 cells/kg (Range 1.78-16.99 x 106 CAR T-cells/kg). Four patients had CRS (Grade I / II), and all of them responded to a single dose of Tocilizumab (8 mg/Kg). Late-onset cytopenias was recorded in 1 patient. There were no ICANS events, dose-limiting toxicities, or deaths related to HCAR 19. The median duration of hospitalization for toxicity was 6 days (Range: 0-22). The dose, response, and adverse events are summarized in Table 1.
After a median follow-up of 4.5 months (Range 2- 12 months), 3 had complete response, 1 had partial response, 1 had stable disease and 3 had disease progression. All patients with responses are alive at follow up (range: 60-300 days). There were 3 deaths due to disease progression. 3 out of 10 patients had hypogammaglobulinemia at baseline and required IVIG replacement, none of the other patients required the replacement. The CART expansion kinetics is depicted in Fig 1.
Conclusions HCAR19 is safe and active with manageable toxicities in patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma. The favorable safety profile may allow delivery in an outpatient setting and in a cost-effective manner particularly critical to the delivery of CAR T-cells in LMIC countries.
Disclosures
Jain:Cipla Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd: Research Funding; Zydus Lifesciences Ltd: Research Funding; Intas Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd, Cipla Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd: Research Funding; ImmunoAdaptive Therapy Pvt Ltd: Research Funding. Karulkar:Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment. Shah:ImmunoAdaptive Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment. Firfiray:Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment. Kalra:ImmunoAdaptive Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment. Ravikumar:ImmunoAdoptive Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment. Purwar:Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Pvt Ltd: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. Neelapu:Bluebird Bio: Consultancy, Honoraria; Unum Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Calibr: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Adicet Bio: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Legend Biotech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Cell Medica/Kuur: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Allogene Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Medscape: Consultancy, Honoraria; Aptitude Health: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bio Ascend: Consultancy, Honoraria; Poseida: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Karus Therapeutics: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Patents & Royalties: related to cell therapy..
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal